Cataract Disease: Understanding, Preventing, and Treating in Geneva
Focus Keyphrase: Cataract Disease Geneva
SEO Title (English): Cataract Geneva: Symptoms, Treatments & Surgery
SEO Description (English): Learn about cataracts in Geneva. Discover the symptoms, surgical treatment options and prevention tips. Your ophthalmology practice in Geneva is here to help.
What is a Cataract? Simple Definition
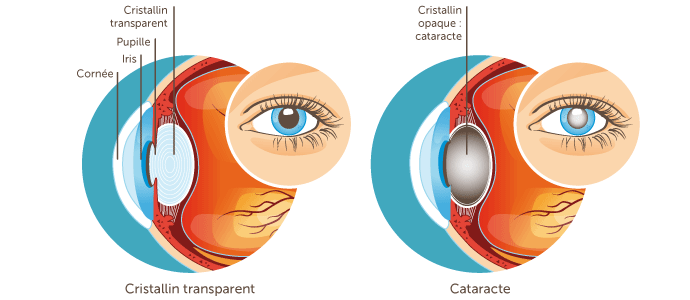
A cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye, the natural lens located behind the iris and pupil. Imagine the lens as the lens of a camera. When it becomes cloudy, like frosted glass, light can no longer pass through clearly, blurring vision.
A cataract is not a membrane that forms over the eye, but rather an internal change in the lens itself. It is a process generally related to aging, but other factors can contribute to its development.
Symptoms of Cataracts: How to Recognize Them?
Cataract development is progressive, and symptoms may appear gradually. The most common signs of cataracts include:
- Cloudy or blurry vision: Like looking through a veil or fog.
- Glare: Increased sensitivity to bright light, car headlights, sunlight, with halos around light sources.
- Double vision (diplopia) in one eye (rare).
- Difficulty seeing at night or in low light conditions.
- Color fading: Colors may appear less vibrant, duller, or yellowish.
- Frequent changes in eyeglass prescription: Needing to change glasses more often than before.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other eye problems. Only a comprehensive eye exam can confirm a diagnosis of cataracts.
Causes and Risk Factors for Cataracts
The most common cause of cataracts is the natural aging of the lens. With age, the proteins that make up the lens clump together and denature, leading to clouding. However, other factors can accelerate or promote cataract development:
- Age: The risk increases significantly with age, especially after 60.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing cataracts.
- Smoking.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Eye injuries: Shock, injury to the eye.
- Prolonged use of certain medications: Corticosteroids, for example.
- Family history of cataracts.
- High myopia (severe nearsightedness).
- Certain systemic diseases.
Identifying risk factors can help in adopting preventive measures and regularly monitoring your eye health.
Diagnosis of Cataracts: The Eye Examination
Cataract diagnosis is usually made during a comprehensive eye examination. This exam will include:
- Visual acuity measurement: To assess the quality of your vision at different distances.
- Slit-lamp examination: A specialized microscope used to examine the structures of the eye in detail, including the lens, and visualize clouding.
- Fundus examination (ophthalmoscopy): After pupil dilation, to examine the retina and optic nerve, and rule out other causes of vision loss.
- Tonometry: Measurement of intraocular pressure to screen for glaucoma.
These examinations are painless and allow your ophthalmologist to determine the presence, type, and stage of cataracts, as well as assess your eligibility for surgery.
Treatment of Cataracts: Surgery
The only effective treatment for cataracts is surgery. There are no medications, eye drops, or glasses that can cure or eliminate cataracts. Cataract surgery is one of the most commonly performed and safest surgical procedures worldwide.
Principles of surgery:
- Anesthesia: Local (eye drops or injection around the eye) or general (rarer).
- Micro-incision: A very small incision (a few millimeters) is made in the cornea.
- Phacoemulsification: The clouded lens is fragmented using ultrasound and aspirated.
- Artificial lens implant (intraocular lens implant - IOL): A clear artificial lens is inserted to replace the clouded natural lens. There are different types of implants (monofocal, multifocal, toric) tailored to each patient's needs.
- Incision closure: The incision is so small that it usually self-seals, without sutures in most cases.
Cataract surgery is generally quick (about 15-30 minutes), performed on an outpatient basis (you go home the same day), and allows for rapid visual recovery in most cases.
After Cataract Surgery: Postoperative Care
Postoperative care after cataract surgery is usually straightforward. It is normal to experience mild discomfort, a gritty sensation, or slightly blurred vision for the first few days. Anti-inflammatory and antibiotic eye drops are prescribed to prevent infection and promote healing.
Postoperative advice:
- Strictly follow eye drop prescriptions.
- Avoid rubbing or touching the operated eye.
- Wear a protective shield at night for a few days.
- Avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, and water activities for a few weeks.
- Protect your eyes from the sun with sunglasses.
- Keep postoperative follow-up appointments with your ophthalmologist.
Visual recovery gradually improves in the weeks following surgery. The vast majority of patients regain clear and improved vision after cataract surgery.
Cataract Prevention: Useful Tips
Although it is impossible to completely prevent age-related cataracts, certain measures can help slow their progression and protect your eye health:
- Wear sunglasses that provide 100% UVA and UVB protection, even on cloudy days.
- Quit smoking. Smoking is a significant risk factor.
- Adopt a healthy and balanced diet, rich in antioxidant fruits and vegetables (vitamins C and E, carotenoids).
- Control your blood sugar levels if you have diabetes.
- Limit your alcohol consumption.
- Have regular eye exams, especially after age 50, for early detection.
Prevention and early detection are essential to preserve good vision throughout life.
Cataracts and Your Vision in Geneva: Our Expertise at Your Service
If you think you may have cataracts or are experiencing worrying visual symptoms, it is important to consult an ophthalmologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. Our ophthalmology practice in Geneva specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of cataracts, as well as all eye conditions.
[Your Ophthalmology Practice Name]
[Your Practice Address in Geneva]
[Phone Number]
[Website (if applicable)]
Consult our ophthalmology practice for medical advice on your case. Book your appointment with us over the phone +41 (0) 22 346 26 78 or through our online booking.



Leave a Comment